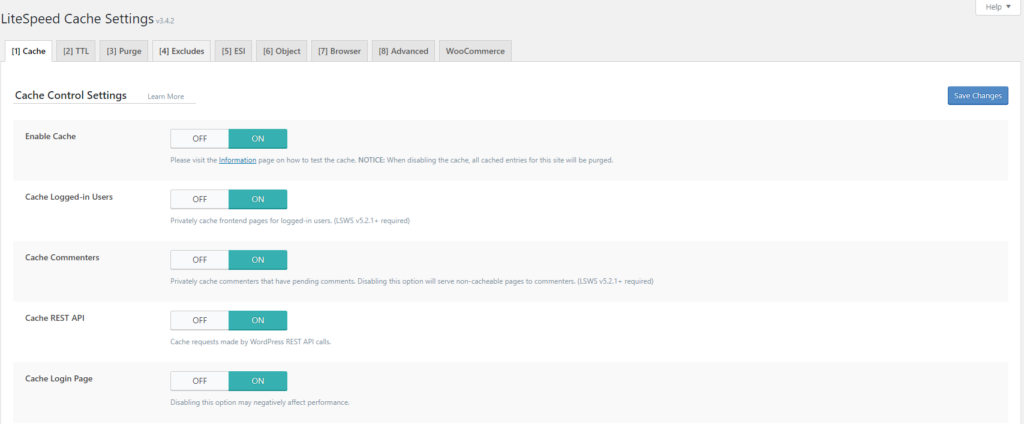
The options shown are enabled at startup like the others. There is not much explanation in this part because the option itself tells what kind of caching we are talking about.
Cache Logged-in User: When this option is enabled each page will be separately cached for each logged in user separately and will be served to them. Private cache.
What I would like to mention in this first part is that if you turn off the first Enable cache option, you will delete all the cache that has been created.
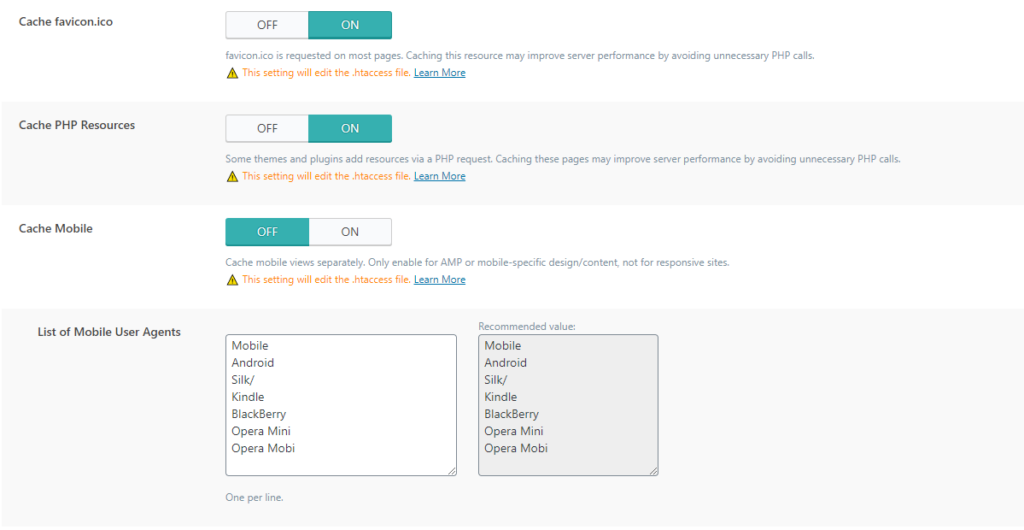
Cache Mobile: In this option paying attention to Cache mobile. Turn on this option if you have a separate mobile version of the site or AMP. If you have a theme that is responsive, then do not include it because it means that it can load the mobile layout on some computer and thus disrupt the loading layout.
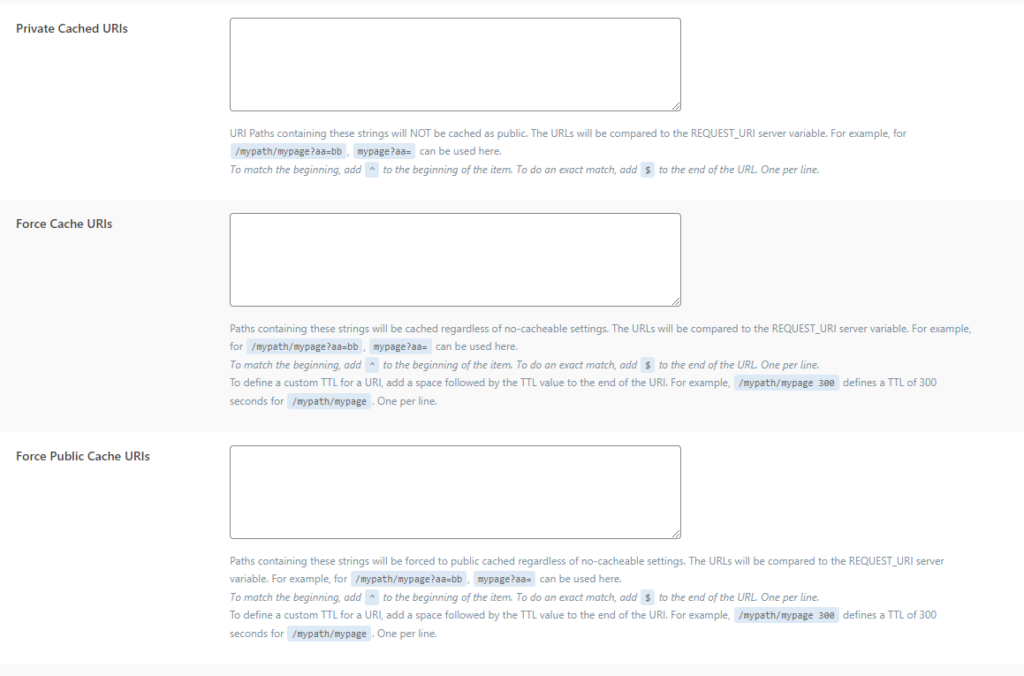
Private cache URL: this option is important if you want to include a private cache for individual pages. It can be used for pages that users should not see or for pages where each visitor should see a different version of the page and in other extremely rare cases.
Force Cache URL: This option is used to cache pages regardless of settings. The urls you post here will be cached completely. Depending on other options, it will be cached as private or public.
Force Public Cache URL: In this option you put pages that will be cached exclusively as public cache.
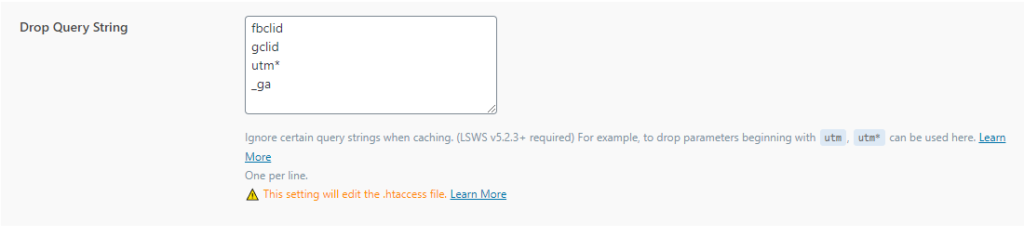
Drop Query String: In this option, you ignore redundant queries in the link so that they are not cached as separate pages. If you have another query that you use on the site and does not affect the content of the page, you can add it here.

